Extending Configuration Support
1. Custom ConfigSource
It’s possible to create a custom ConfigSource as specified in
MicroProfile
Config.
With a Custom ConfigSource it is possible to read additional configuration
values and add them to the Config instance in a defined ordinal. This
allows overriding values from other sources or falling back to other values.
A custom ConfigSource requires an implementation of
org.eclipse.microprofile.config.spi.ConfigSource or
org.eclipse.microprofile.config.spi.ConfigSourceProvider. Each
implementation requires registration via the
ServiceLoader
mechanism, either in
META-INF/services/org.eclipse.microprofile.config.spi.ConfigSource or
META-INF/services/org.eclipse.microprofile.config.spi.ConfigSourceProvider
files.
1.1. Example
Consider a simple in-memory ConfigSource:
package org.acme.config;
import org.eclipse.microprofile.config.spi.ConfigSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class InMemoryConfigSource implements ConfigSource {
private static final Map<String, String> configuration = new HashMap<>();
static {
configuration.put("my.prop", "1234");
}
@Override
public int getOrdinal() {
return 275;
}
@Override
public Set<String> getPropertyNames() {
return configuration.keySet();
}
@Override
public String getValue(final String propertyName) {
return configuration.get(propertyName);
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return InMemoryConfigSource.class.getSimpleName();
}
}And registration in:
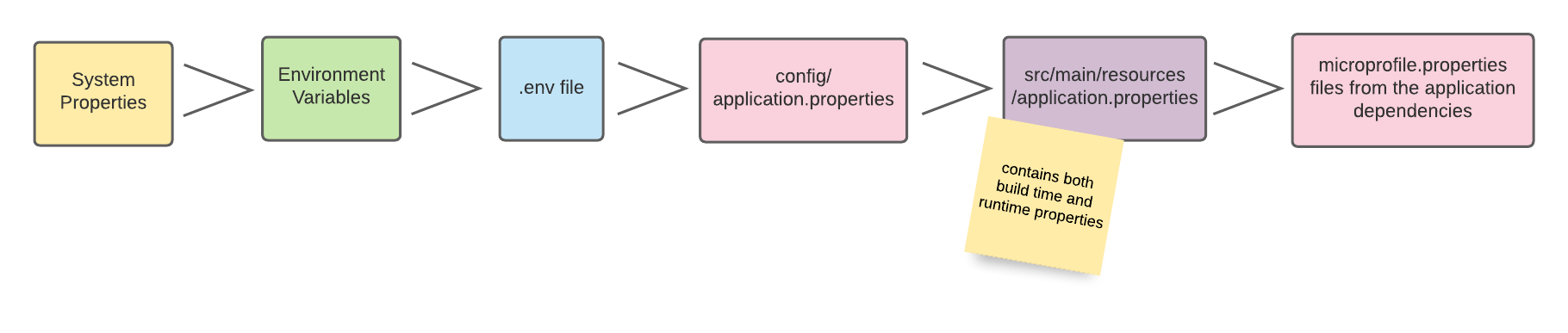
org.acme.config.InMemoryConfigSourceThe InMemoryConfigSource will be ordered between the .env source, and
the application.properties source due to the 275 ordinal:
ConfigSource |
Ordinal |
System Properties |
400 |
Environment Variables from System |
300 |
Environment Variables from |
295 |
InMemoryConfigSource |
275 |
|
260 |
|
250 |
|
100 |
In this case, my.prop from InMemoryConfigSource will only be used if the
config engine is unable to find a value in
System Properties,
Environment Variables from
System or Environment Variables from
.env file in this order.
1.2. ConfigSource Init
When a Quarkus application starts, a ConfigSource can be initialized
twice. One time for STATIC INIT and a second time for RUNTIME INIT:
1.2.1. STATIC INIT
Quarkus starts some of its services during static initialization, and
Config is usually one of the first things that is created. In certain
situations it may not be possible to add a custom ConfigSource. For
instance, if the ConfigSource requires other services, like a database
access, it will not be available at this stage, and cause a chicken-egg
problem. For this reason, any custom ConfigSource requires the annotation
@io.quarkus.runtime.configuration.StaticInitSafe to mark the source as
safe to be used at this stage.
1.2.1.1. Example
Consider:
package org.acme.config;
import org.eclipse.microprofile.config.spi.ConfigSource;
import io.quarkus.runtime.annotations.StaticInitSafe;
@StaticInitSafe
public class InMemoryConfigSource implements ConfigSource {
}And registration in:
org.acme.config.InMemoryConfigSourceThe InMemoryConfigSource will be available during STATIC INIT.
A custom ConfigSource is not automatically added during Quarkus STATIC
INIT. It requires to be marked with the
@io.quarkus.runtime.configuration.StaticInitSafe annotation.
|
2. ConfigSourceFactory
Another way to create a ConfigSource is via the
SmallRye Config
io.smallrye.config.ConfigSourceFactory API. The difference between the
SmallRye Config factory and the
standard way to create a ConfigSource as specified in
MicroProfile
Config, is the factory ability to provide a context with access to the
available configuration.
Each implementation of io.smallrye.config.ConfigSourceFactory requires
registration via the
ServiceLoader
mechanism in the META-INF/services/io.smallrye.config.ConfigSourceFactory
file.
2.1. Example
Consider:
package org.acme.config;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.OptionalInt;
import org.eclipse.microprofile.config.spi.ConfigSource;
import io.smallrye.config.ConfigSourceContext;
import io.smallrye.config.ConfigSourceFactory;
import io.smallrye.config.ConfigValue;
import io.smallrye.config.PropertiesConfigSource;
public class URLConfigSourceFactory implements ConfigSourceFactory {
@Override
public Iterable<ConfigSource> getConfigSources(final ConfigSourceContext context) {
final ConfigValue value = context.getValue("config.url");
if (value == null || value.getValue() == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
try {
return Collections.singletonList(new PropertiesConfigSource(new URL(value.getValue())));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public OptionalInt getPriority() {
return OptionalInt.of(290);
}
}And registration in:
org.acme.config.URLConfigSourceFactoryBy implementing io.smallrye.config.ConfigSourceFactory, a list of
ConfigSource may be provided via the Iterable<ConfigSource>
getConfigSources(ConfigSourceContext context) method. The
ConfigSourceFactory may also assign a priority by overriding the method
OptionalInt getPriority(). The priority values is used to sort multiple
io.smallrye.config.ConfigSourceFactory (if found).
io.smallrye.config.ConfigSourceFactory priority does not affect the
ConfigSource ordinal. These are sorted independently.
|
When the Factory is initializing, the provided ConfigSourceContext may
call the method ConfigValue getValue(String name). This method looks up
configuration names in all ConfigSources that were already initialized
by the Config instance, including sources with lower ordinals than the
ones defined in the ConfigSourceFactory. The ConfigSource list provided
by a ConfigSourceFactory is not taken into consideration to configure
other sources produced by a lower priority ConfigSourceFactory.
3. Custom Converter
It is possible to create a custom Converter type as specified by
MicroProfile
Config.
A custom Converter requires an implementation of
org.eclipse.microprofile.config.spi.Converter<T>. Each implementation
requires registration via the
ServiceLoader
mechanism in the
META-INF/services/org.eclipse.microprofile.config.spi.Converter
file. Consider:
package org.acme.config;
public class MicroProfileCustomValue {
private final int number;
public MicroProfileCustomValue(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
}The corresponding converter will look similar to the one below.
package org.acme.config;
import org.eclipse.microprofile.config.spi.Converter;
public class MicroProfileCustomValueConverter implements Converter<MicroProfileCustomValue> {
@Override
public MicroProfileCustomValue convert(String value) {
return new MicroProfileCustomValue(Integer.parseInt(value));
}
}
The custom converter class must be public, must have a public
constructor with no arguments, and must not be abstract.
|
The custom configuration type converts the configuration value automatically:
@ConfigProperty(name = "configuration.value.name")
MicroProfileCustomValue value;3.1. Converter priority
The jakarta.annotation.Priority annotation overrides the Converter
priority and change converters precedence to fine tune the execution
order. By default, if no @Priority is specified by the Converter, the
converter is registered with a priority of 100. Consider:
package org.acme.config;
import jakarta.annotation.Priority;
import org.eclipse.microprofile.config.spi.Converter;
@Priority(150)
public class MyCustomConverter implements Converter<MicroProfileCustomValue> {
@Override
public MicroProfileCustomValue convert(String value) {
final int secretNumber;
if (value.startsFrom("OBF:")) {
secretNumber = Integer.parseInt(SecretDecoder.decode(value));
} else {
secretNumber = Integer.parseInt(value);
}
return new MicroProfileCustomValue(secretNumber);
}
}Since it converts the same value type (MicroProfileCustomValue) and has a
priority of 150, it will be used instead of a
MicroProfileCustomValueConverter which has a default priority of 100.
All Quarkus core converters use the priority value of 200. To override any
Quarkus specific converter, the priority value should be higher than 200.
|
4. Config Interceptors
SmallRye Config provides an interceptor chain that hooks into the configuration values resolution. This is useful to implement features like Profiles, Property Expressions, or just logging to find out where the config value was loaded from.
An interceptor requires an implementation of
io.smallrye.config.ConfigSourceInterceptor. Each implementation requires
registration via the
ServiceLoader
mechanism in the
META-INF/services/io.smallrye.config.ConfigSourceInterceptor file.
The io.smallrye.config.ConfigSourceInterceptor is able to intercept the
resolution of a configuration name with the method ConfigValue
getValue(ConfigSourceInterceptorContext context, String name). The
ConfigSourceInterceptorContext is used to proceed with the interceptor
chain. The chain can be short-circuited by returning an instance of
io.smallrye.config.ConfigValue. The ConfigValue objects hold information
about the key name, value, config source origin and ordinal.
| The interceptor chain is applied before any conversion is performed on the configuration value. |
Interceptors may also be created with an implementation of
io.smallrye.config.ConfigSourceInterceptorFactory. Each implementation
requires registration via the
ServiceLoader
mechanism in the
META-INF/services/io.smallrye.config.ConfigSourceInterceptorFactory file.
The ConfigSourceInterceptorFactory may initialize an interceptor with
access to the current chain (so it can be used to configure the interceptor
and retrieve configuration values) and set the priority.
4.1. Example
package org.acme.config;
import static io.smallrye.config.SecretKeys.doLocked;
import jakarta.annotation.Priority;
import io.smallrye.config.ConfigSourceInterceptor;
import io.smallrye.config.ConfigLogging;
@Priority(Priorities.LIBRARY + 200)
public class LoggingConfigSourceInterceptor implements ConfigSourceInterceptor {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 367246512037404779L;
@Override
public ConfigValue getValue(final ConfigSourceInterceptorContext context, final String name) {
ConfigValue configValue = doLocked(() -> context.proceed(name));
if (configValue != null) {
ConfigLogging.log.lookup(configValue.getName(), configValue.getLocation(), configValue.getValue());
} else {
ConfigLogging.log.notFound(name);
}
return configValue;
}
}And registration in:
org.acme.config.LoggingConfigSourceInterceptorThe LoggingConfigSourceInterceptor logs looks up configuration names in
the provided logging platform. The log information includes config name and
value, the config source origin and location if exists.

